Continuous Binomial distribution can be derived from continuous Bernoulli distribution, following the probability distribution relationship between Bernoulli distribution and binomial distribution.
This mathematical derivation is based on the literature of Loaiza-Ganem and Cunningham (2019), who proposed the characteristics of continuous Bernoulli distribution.
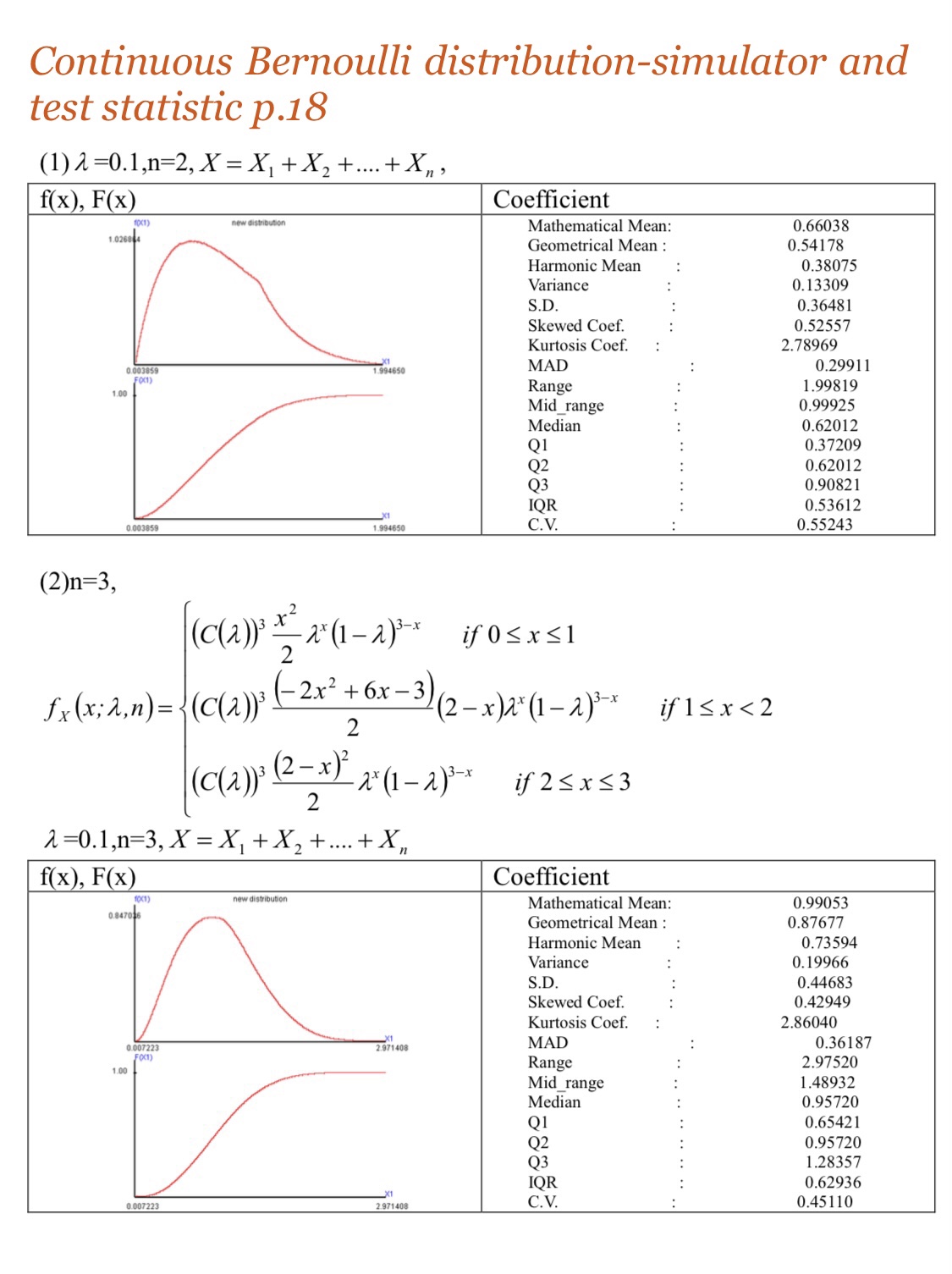
The book named “Continuous Bernoulli distribution-simulator and test statistic” derived the continuous binomial distribution from the case of n=2 to n=5. Then induct the probability density function.

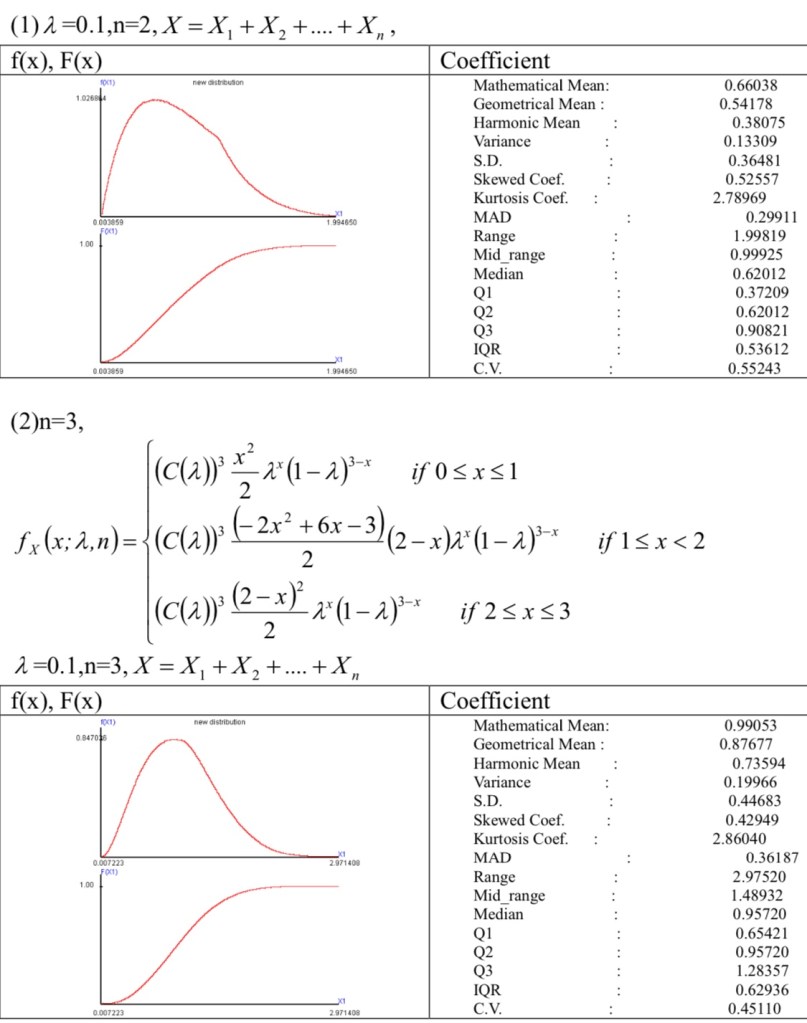
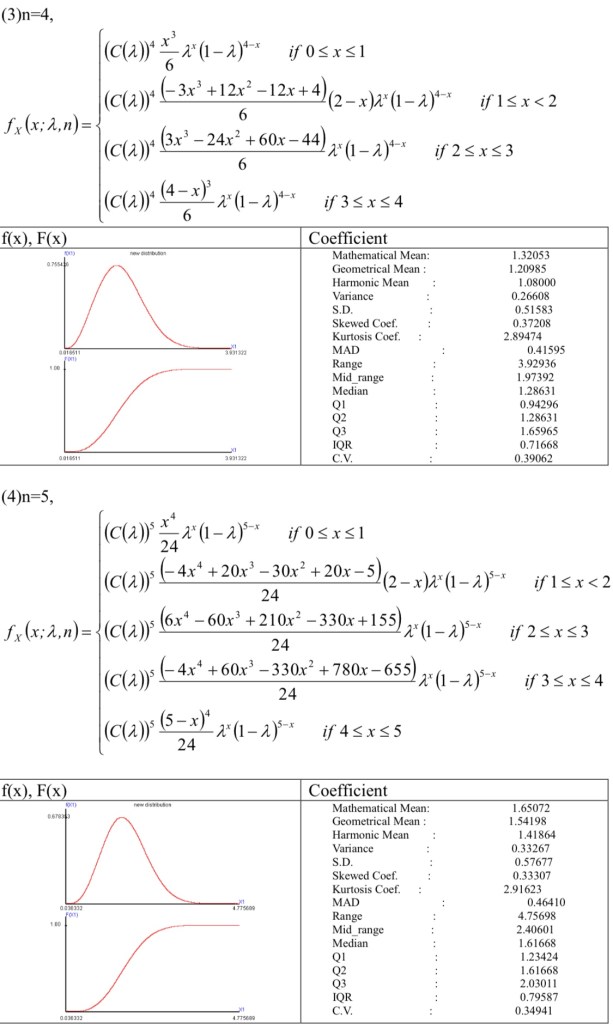
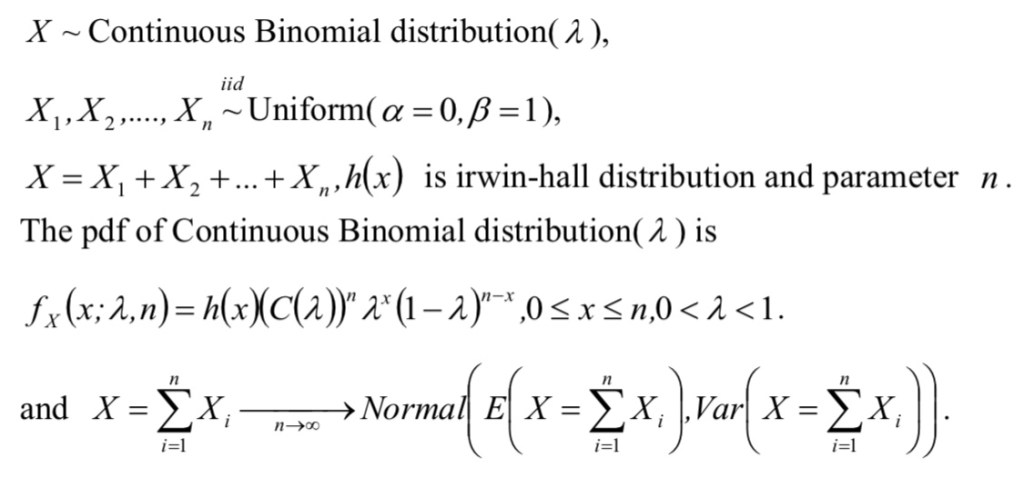
The probability density function of continuous binomial distribution is associated with Irwin-hall distribution and n. Based on the relationship of Bernoulli distribution and binomial distribution, the random variables of continuous Bernoulli distribution is summed as X and approximates to normal distribution.
The book had provided the mathematical derivation and induction of probability density function of continuous binomial distribution. The rest can be read on http://vixra.org/abs/2012.0088.
References
- Irwin-Hall distribution, wiki website: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Irwin–Hall_distribution.
- Loaiza-Ganem, G., and Cunningham, P.J. (2019). The continuous Bernoulli: fixing a pervasive error in variational autoencoders. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 13287-13297.
- Wang, K.S., and Lee, M.Y. (2020). Continuous Bernoulli distribution-simulator and test statistic. Free ebook on Free-ebook.net. https://www.free-ebooks.net/computer-sciences-textbooks/Continuous-Bernoulli-distribution-simulator-and-test-statistic